Breast cancer causes occurs when the DNA in the breast cells is changed, disabling specific functions that control cell growth and division. In many cases, these mutated cells die or attacked by the immune system. But some cells escape from the immune system and grow unrestricted, forming a tumor in the breast.
What Are The Breast Cancer Causes?
Exact breast cancer causes vary person to person. Some risk factors, including obesity, menopause and excessive alcohol consumption, are strongly linked to the disease.
Furthermore, people who inherit mutations in their PRCA1 and PRCA2 genes have a higher risk of developing breast cancer. Known risk factors for breast cancer include:
1) Aging:
On average, women over the age of 60 are more likely to develop breast cancer. It causes only about 10% to 15% of breast cancers in women fewer than 45 years of age. However, this may vary for different females.
2) Gender:
Breast cancer symptoms in men are diagnosed nearly 2000 each year. It is 100 times more common in women. The National Cancer Institute estimates that more than 190,000 women are diagnosed with breast cancer each year.
3) Genetics and Family History:
Having a family history of breast cancer, especially for a mother, sister or a daughter who has or has been diagnosed with breast cancer, can double the risk.
4) Hereditary Factors:
Mutations in the PRCA1 and PRCA2 genes are the most common genetic causes. Other rare mutations can also cause some women to develop breast cancer. Genetic testing reveals the presence of potential genetic problems, especially in families with a history of breast cancer.
5) Obesity:
After menopause, adipose tissue may contribute to increased estrogen levels, and higher levels of estrogen may increase the risk of breast cancer. Weight gain in adulthood and excess body fat around the waist may play a role.
6) Childlessness:
Women who do not have children or women who become pregnant later (over the age of 35) are more likely to develop breast cancer. Breastfeeding can help reduce your risk of breast cancer.
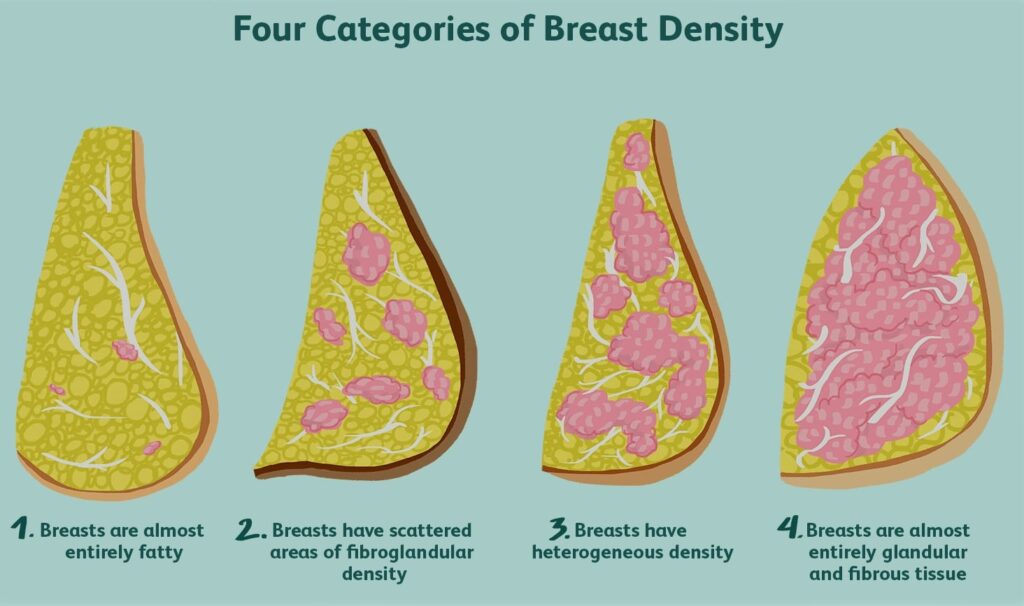
7) High Breast Density:
Women with low fat tissue and high glandular and fibrous tissue have a higher risk of developing breast cancer than women with low density breasts.
8) Menstrual History:
Women who start menstruating at an early age (before the age of 12) have a slightly higher risk of breast cancer. Prolonged exposure to the hormones estrogen and progesterone increases the risk.
9) Excessive Drinking:
Alcohol use is associated with an increased risk of developing breast cancer. Alcohol consumption increases the risk.
10) Birth Control Pills:
The use of oral contraceptives in the last 10 years may slightly increase the risk of developing breast cancer. Once the pills stopped, the risk decreases over time.
11) Combined Menopausal Hormone Therapy (PHT):
The use of combination hormone therapy after menopause increases the risk of developing breast cancer. Combined MHT also increases the chance of seeing cancer at a more advanced stage.
12) Diethylstilbestrol Expression (DES):
Pre-use of DES, a drug commonly given to pregnant women from 1940 to 1971 to prevent miscarriage may slightly increase the risk of developing breast cancer. Females whose mothers took DES during pregnancy, have a slightly higher risk of breast cancer causes.
13) Radiation Exposure:
Women who have received radiation treatment to the breast area, such as progenies or adolescents, have a significantly increased risk of breast cancer treatment for another cancer.
Types Of Breast Cancer
What Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer?
Inflammatory breast cancer (IPC) is rare and accounts for only 1-5% of all breast cancers. Although it is often a type of invasive vascular cancer, it differs from other types of breast cancer in its symptoms, outlook and treatment. IPC has inflammation symptoms such as swelling and redness, but infection or injury does not cause IPC or symptoms.
Cancer cells “swell” the breast by blocking the lymphatic vessels in the skin. Symptoms include swelling of the breast, purple or redness of the skin, and pale or thickening of the breast’s skin, which may look like orange peel.
Often, you will not feel breast cancer lump. If you have any of these symptoms, it does not mean you have IPC, but you should immediately see a doctor.
What Is Triple Negative Breast Cancer?
The term triple-negative breast cancer refers to the fact that cancer cells do not contain estrogen or progesterone receptors. It does not produce much of a protein called HER2. These cancers are more common in women under 40, African-Americans, or women with PRCA1 mutation.
Triple-negative breast cancer causes (DNBC) accounts for about 10-15% of all cancers. Triple-negative differs from other types of invasive breast cancer in that they grow and spread rapidly, have limited treatment options, and have a poor outcome.
What Is Stage 1 Breast Cancer?
This breast cancer is an early stage of invasive breast cancer. In stage I, the tumor measures up to 2 cm and has no lymph nodes. The cancer cells spread from the original location and into the surrounding tissue.
Because stage 1 tumor is small, it isn’t easy to diagnose. However, breast self-examinations and routine screening are always essential and can often lead to an early diagnosis when the cancer is favorably treated.
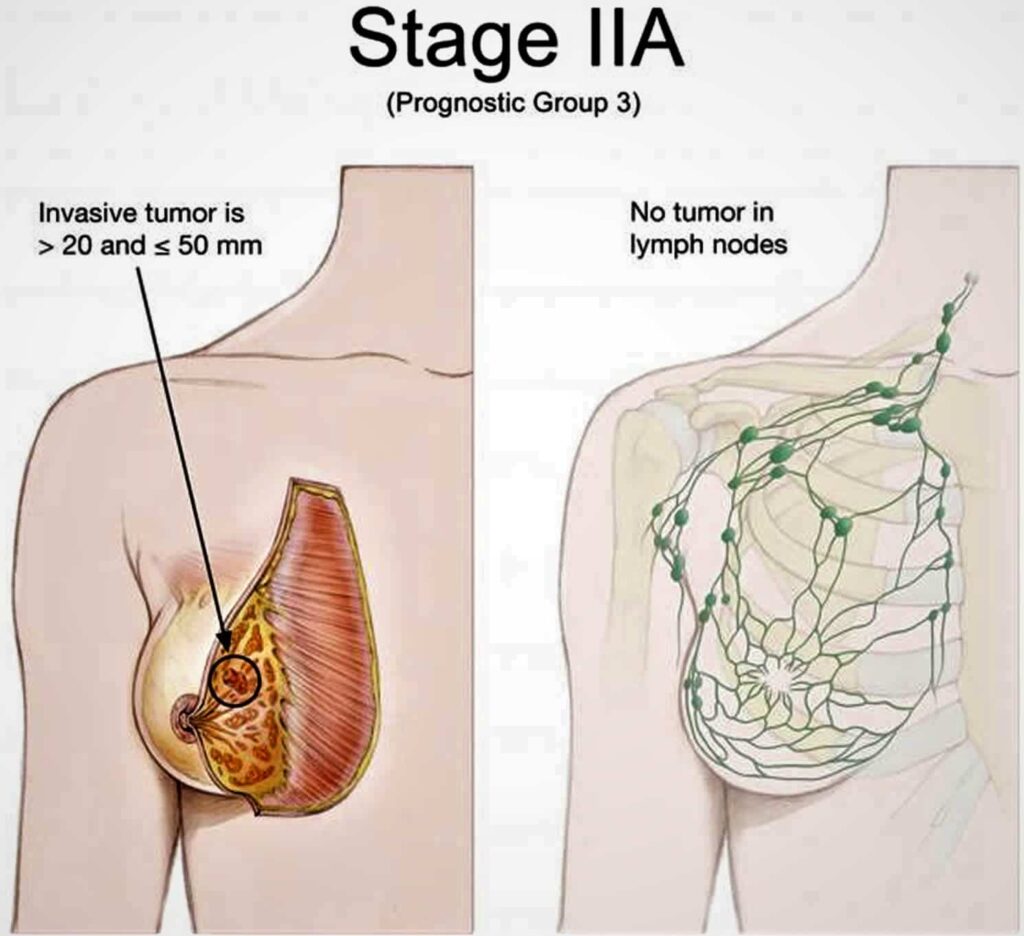
What Is Stage 2 Breast Cancer?
At this stage, the tumor measures 2 cm to 5 cm, or cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm on the same side of the breast. Stage 2 refers to a slightly advanced form of breast cancer. The cancer cells have spread beyond the original location and into the surrounding breast tissue, and the tumor is more extensive than in tumor stage 1 disease.
However, secondary cancer does not spread to distant parts of the body. Breast self-examinations and regular screening are always necessary and can often lead to an early diagnosis when cancer is highly treated.
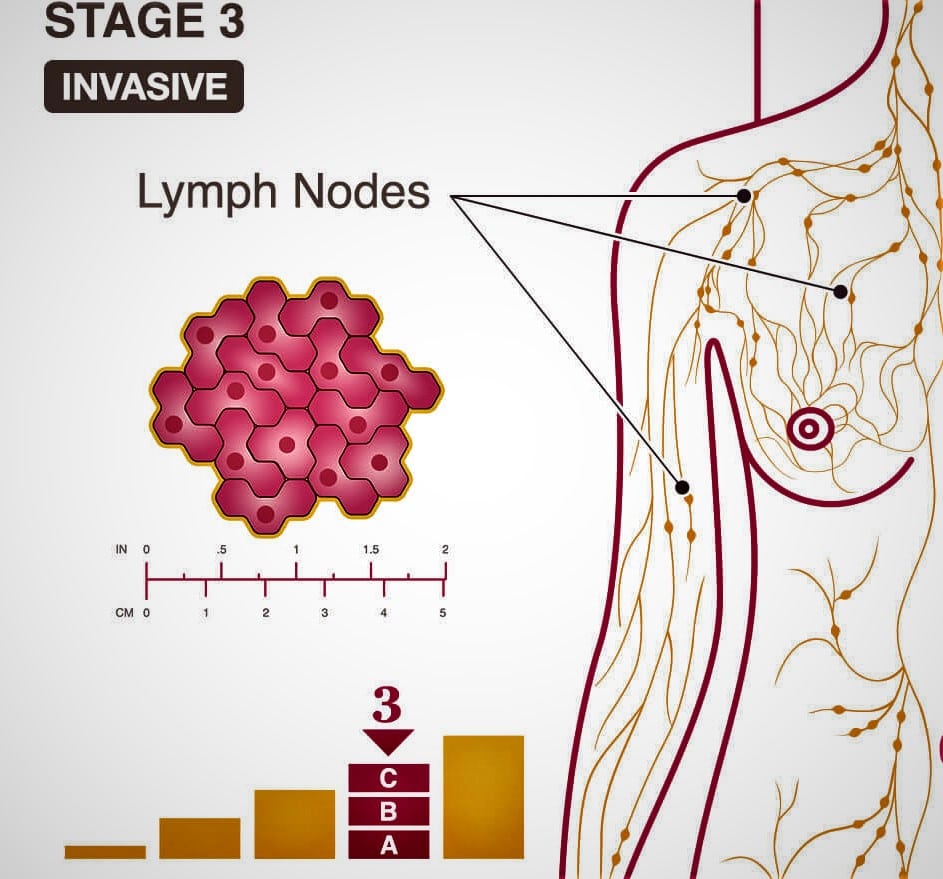
What Is Stage 3 Breast Cancer?
The tumor at this stage of breast cancer is more than 2 inches in diameter, and cancer has spread to the abdominal lymph nodes or other lymph nodes or tissues near the breast. A stage 3 breast cancer is the most advanced form of invasive breast cancer.
At this stage, the cancer cells usually do not spread to more distant parts of the body, but they do have many axial (footer) lymph nodes. At this point, the tumor may be very large, extending to the chest wall or the breast’s skin.
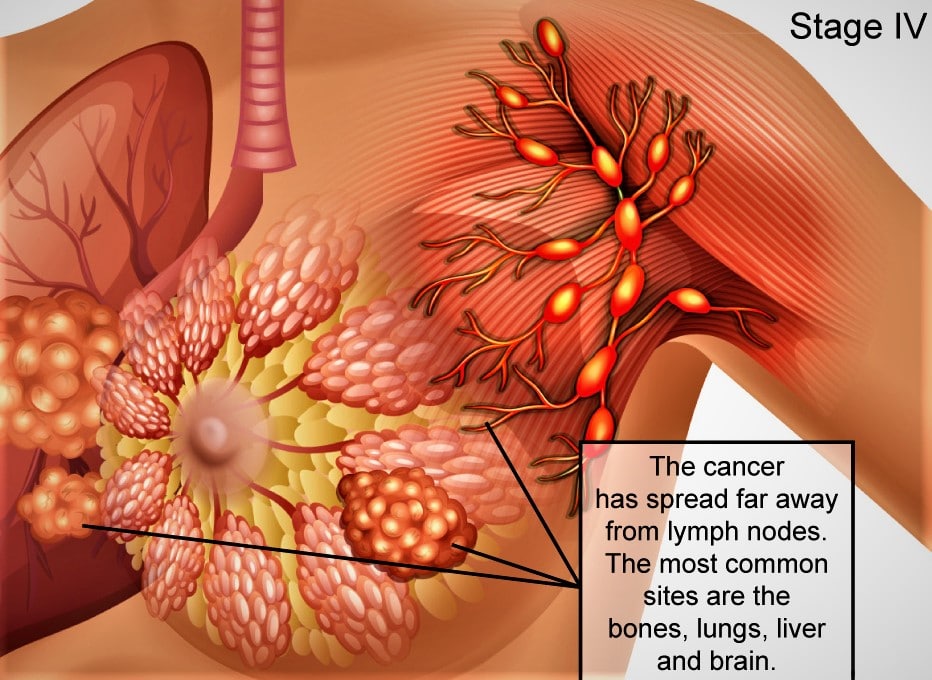
What Is Stage 4 Breast Cancer?
This stage, also known as metastatic breast cancer, is when cancer spreads to or near the breast to other parts of the body beyond the mammary glands, abdomen and internal mammary glands. Cancer has spread to other parts of the body. Affected areas may include bones, brain, lungs, or liver, and may involve more than one area of the body.
In stage IV, DNM positions help to describe the extent of the disease. Higher numbers indicate a more comprehensive condition. In general, stage 4 breast cancer causes are defined as:
- D1, D2, D3 or D4, depending on the size of the primary tumor.
- M1: The disease has spread to other sites in the body
- N1: Cancer has spread to the lymph nodes