Last updated on June 24th, 2025 at 12:36 pm
Some people may have a higher risk of sexual and reproductive health issues because of genetic factors.
In contrast, others may have greater risk factors due to factors that they may not be aware of, such as using certain medications, medical conditions, or living in an environment that may put them at risk. Factors that may increase sexual health risk need to address with counseling. Medical treatment for sexual partners, especially when sexual activity involved.
Sexual Health
Sexual health is a state of physical, emotional, and social well-being with sexuality. Here is the possibility of having pleasurable and safe sexual experiences, free of pressure, taste, discrimination, and confusion.
Sexual health needs a positive, confident, and respectful approach to sexuality and sexual relationships. For sexual health to achieved and managed, all persons’ sexual rights must be protected, respected, and satisfied.
Compelling communications contain various attributes meant to enhance seduction, including an attractive source. A message containing convincing thoughts, or efforts to make the topic look personally relevant to the partner.
Factors That May Raise Risk Of Disease
During your teens, you went through puberty and became sexually matured. If you are a girl, enlarge your breasts and begin to get your period. If you are a boy, your penis and testicles become large and strong.
In case you have sex, then you might get pregnant or make pregnant someone. Whether you wish to have sex or not, it is good to know about safe sex and how sex affects your health.
During pregnancy, having sex puts you at risk of getting a sexually transmitted disease (STD), such as:
- Chlamydia
- HPV
- Gonorrhea
- Syphilis
- Genital Herpes
- Human Papillomavirus
- HIV/AIDS
The only way to be safe and want to have any sexual contact is a condom. Latex condoms are the most reliable protection against sexually transmitted infections. Condoms are also used for birth control to prevent pregnancy. They prepared and available in lubricated or non-lubricated, as well as with spermicide or without it.
Sexual activity, smoking, hypertension, cigarette smoking, and alcohol use can raise the risk factors for sexual and reproductive health issues and are also associated with heart disease.
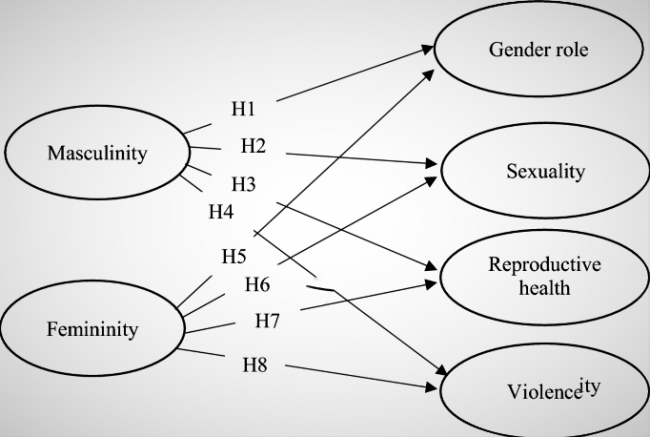
Gender Aspect of Sexual Reproductive Health
Sexual health belongs to a well-being state that lets a woman engage entirely in and enjoy sexual activity. A variety of physical, psychological, interpersonal, and social factors impact a woman’s sexual health.
In the perspective of overall health, it can notice as both a satisfaction source and a sense of well-being, and a potential anxiety source. Being prepared to perform well sexually and be a competent partner in a sexual relationship is a core value for most men. For many, it’s an essential part of their feeling as a man.
As a result, sexual dysfunction can cause discomfort when a man feels that he cannot perform effectively and cannot meet his sexual role with a partner. This may lead to escape-avoidance, distancing, and disengagement. His powerful body image, identity, and self-confidence suffer.
Sexual health needs to addressed as part of overall health care. There may be a relationship between sexual health needs and overall health outcomes for men and women.
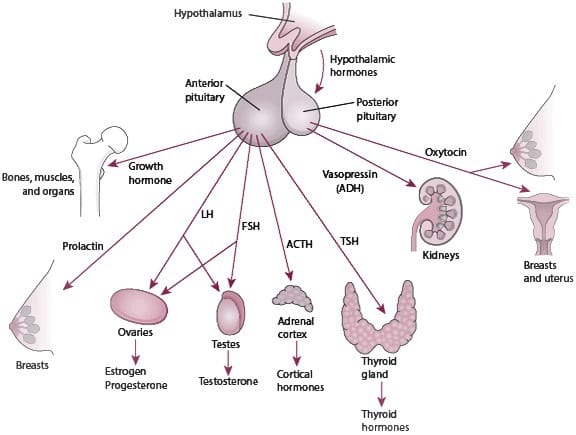
Hormones and Your Heart Conditions
Sex is an essential part of life. Women thinking about sex starts early, often before puberty, and remain until their final days on earth. Sex is just a different hormone-driven bodily function plan to preserve the species. It is a pleasurable activity that connects two people and makes a strong bonding between them.
Sex hormones and your heart can be the cause of many physical conditions, some of them life-threatening. High levels of circulating sex hormones like androgens (including testosterone, human growth hormone, and female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone). These are associating with an increased risk for atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) and coronary artery disease (hardening of the arteries in the heart). This condition is known as atherosclerotic disease.
Other physical conditions such as breast cancer, colon cancer, gallbladder disease, kidney disease, cervical cancer, head injury, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, high cholesterol, and oral contraceptives may also linked to higher risk in sex hormones and your heart.
Sex requires powerful connections between the sex organs, hormone-producing glands, the brain, and the rest of the body. If one part is out of stroke, the desire for sex may decrease, or the ability to have sex may be compromised.
In addition to the physical and biochemical capabilities at work, a woman’s activities, expectations, mental health, and emotional health grow her sexuality.
Does Your Vagina Need Probiotics?
Vaginal probiotic supplements are hugely common. These are available these days in drinks, pills, and syrups. Marketers suggest that you need to take them not only for your stomach but also for your vagina.
Many women are noticing the message, said by Doctors. This includes both probiotic pills and supplementary medicines that injected into the vagina using an applicator.
The natural decrease in sex hormone levels sometimes causes undesirable symptoms like hot flashes or low sex journeys. Doctors can prescribe pills, gels, and creams carrying estrogen or testosterone to eliminate those symptoms.
Teen Sexual Health
The pregnancy rate has raised steadily across the United States among both married and single women. In some states, the pregnancy rates have been particularly alarming, with teen pregnancy the highest on record.
The increasing rates of teenage pregnancy are troubling in the health care system as it often occurs in communities with higher poverty rates and lower educational levels. Sexual education is becoming more important in the lives of all Americans.
It should made a priority in every state as it decreases teen pregnancy and the rates of STD’s. STD’s are a leading cause of death among adults. So, increasing access to STD testing and treatment is a necessity in this country.
ISSUES IN REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH
Being a woman has health implications. Women’s health needs can broadly be classified under four categories (Fattallah, 1997).
First, women have specific health needs related to sexual and reproductive function.
Second, women have an extensive reproductive system that can be susceptible to dysfunction or disease, even before or after it is removed from the sexual process.
Third, women are subject to the same conditions of other body systems that can affect men. Disease patterns often differ from men due to genetic makeup, hormonal environment, or lifestyle behavior developed by gender. Diseases of other body systems and their treatments may be related to conditions of the reproductive system.
Fourth, because women are women, they are subject to social diseases that impact their physical, mental, and social health.
In function, dysfunction, and disease, the reproductive system plays a focal role in women’s health. This is different from the situation of men. The significant burden of disease in women is related to their reproductive function and reproductive system and how society treats or abuses them due to their gender. Women often suffer because of the natural physiological responsibility to sustain life and its associated tasks.
In a study on investment in health published by the World Bank, a ranking of the five major causes of disease burden on young people in developing countries (aged 15 to 44) showed the following gender differences:
Females | Males |
Sexually-transmitted diseases | Tuberculosis |
Maternal | HIV infection |
Tuberculosis | Homicide and Violence |
HIV infection | Motor vehicle injuries |
Depressive disorders | War |
Sexual Reproductive Health and Rights
Sexual and reproductive rights are necessary for a variety of reasons. Access to safe, affordable, and effective contraceptive methods gives women the opportunity to make informed decisions about their lives. Family planning information and services can improve maternal and child health by helping to prevent unplanned pregnancies among women. Adolescent women are especially at risk for complications during pregnancy. Sexual and reproductive rights can also help prevent HIV and AIDS.
Most maternal deaths are caused by significant complications, including severe bleeding (often postpartum hemorrhage), and infections (usually postpartum); High blood pressure during pregnancy (pre-eclampsia and eclampsia); and unsafe abortion. Prenatal health problems such as malnutrition, high blood pressure, anemia, and malaria also contribute significantly to the risk of neonatal death.
In developing countries, higher pregnancy rates and higher birth rates between the first and adolescence are closely related to the risk of HIV infection and cervical cancer. It is also estimated that unprotected abortions cause 70,000 maternal deaths (13 percent) annually.
In 1994, the International Conference on Population and Development (ICPD) agreed on reproductive health for all by 2015. Although countries have transformed ICPD obligations into policies and practices, access to various family planning options has increased, reduced maternal mortality in some countries, and requires rapid improvement. In 2007, the Global Accessibility Goal for Reproductive Health was added to MDG5.
FAQ’S Related To Sexual Reproductive Health Issues
Reproductive health is a case of entire physical, mental and social well-being and not only the lack of disease or weakness in all matters relating to the reproductive method and its functions and processes.
Common reproductive health concerns for women
• Endometriosis
• Uterine fibroids
• Gynecological cancer
• HIV / AIDS
• Interstitial cystitis
• Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
• STIs (STDs)
Women and girls are especially at risk when the social, health, and other support systems of a region or country collapse, subject to sexual violence, unwanted pregnancy, unsafe abortion, STI (including HIV), and maternal disease and death.
Natural Ways to Boost Reproductive health:
• Eat foods rich in antioxidants. Antioxidants such as foliate and zinc may improve fertility in both men and women
• Eat a more comprehensive breakfast
• Avoid Trans fats
• Cut the corps if you have PCOS
• Eat less refined corps.
• Eat more fiber.
• Change protein sources.
• Choose high-fat milk.






Comments are closed.